Modelling the spread of tree pests and pathogens in urban forests |
| |
| Affiliation: | Department of Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge, Downing Street, Cambridge CB2 3EA, United Kingdom |
| |
| Abstract: | 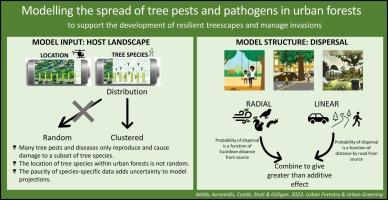
Understanding the potential dynamics of tree pests and pathogens is a vital component for creating resilient urban treescapes. Epidemiologically relevant features include differences in environmental stress and tree management between street and garden trees, and variation in the potential for human-mediated spread due to intensity of human activity, traffic flow and buildings. We extend a standard spatially explicit raster-based model for pest and pathogen spread by dividing the urban tree population into roadside trees and park/garden trees. We also distinguish between naturally-driven radial spread of pests and pathogens and human-mediated linear spread along roads. The model behaviour is explored using landscape data for tree locations in an exemplar UK town. Two main sources of landscape data were available: commercially collated aerial data, which have high coverage but no information on species; and, an urban tree inventory, with low, non-random, coverage but with some species data. The data were insufficient to impute a species-specific host landscape accurately; however, by combining the two data sources, and applying either random or Matérn cluster point process driven selection of a subset of all trees, we create two sets of potential host landscapes. We find that combining the two mechanisms of dispersal has a non-additive effect, with the enhanced linear dispersal enabling new foci of infection to be established more rapidly than with radial dispersal alone; and clustering of trees by species slows down the expansion of epidemics when compared with random distribution of tree species within known host locations. |
| |
| Keywords: | Mathematical model Urban forestry Tree pests and pathogens Tree inventories Dispersal |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

