Isolation and relative stereochemistry of lippialactone,a new antimalarial compound from Lippia javanica |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Chemistry, University of Venda, Private Bag X5050, Thohoyandou, 0950, South Africa;2. Department of Chemistry, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, 0002, South Africa;1. Centre of Excellence for Pharmaceutical Sciences, North-West University, Private Bag X6001, Potchefstroom, 2520, South Africa;2. Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute, Socinstrasse 57, P.O. Box, 4002, Basel, Switzerland;3. University of Basel, Petersplatz 1, P.O. Box, 4001, Basel, Switzerland;1. School of Pharmacy, University of Oslo, Norway;2. Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway;3. Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University, George, South Africa;4. Chemistry department, University of the Western Cape, Bellville, South Africa |
| |
| Abstract: | 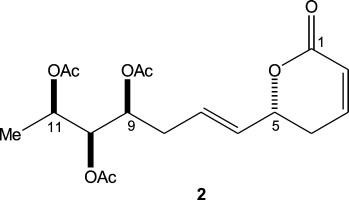
The aerial parts of Lippia javanica were investigated for biologically active chemical compounds present in them. Chromatographic separation of the ethyl acetate extract of the aerial parts yielded a new antimalarial α-pyrone, lippialactone (2). Lippialactone is active against the chloroquine-sensitive D10 strain of Plasmodium falciparum with an IC50 value of 9.1 μg/mL, and is also mildly cytotoxic. The relative stereochemistry of lippialactone was determined by molecular modeling based on the determination of the relative configuration by quantum mechanical GIAO 13C chemical shift calculations. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

